The new EU battery regulation ((EU) 2023/1542)
I. The legislative core of the new EU battery regulation: building the world’s most stringent battery regulatory framework
On August 18, 2025, the new EU Battery Regulation (EU) 2023/1542 came into full effect, officially replacing the 2006/66/EC Battery Directive, becoming the first mandatory regulation covering the full life cycle of batteries.135 Its three strategic objectives are:
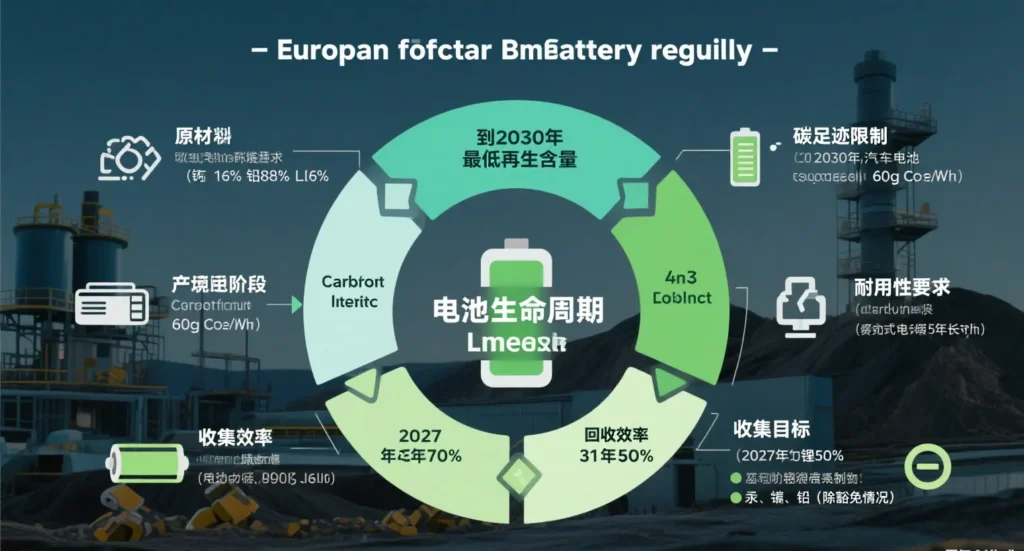
1.Carbon emission reduction: require full life cycle carbon footprint declaration and hierarchical labeling for power batteries
2.Circular economy: set the proportion of key metal recycled materials (lithium ≥ 12% and cobalt ≥ 26% by 2031)
3.Extended Producer Responsibility: strengthen producer’s EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) responsibility for recycling
Key timeline:
- 2025.8.18: EPR registration mandatory, non-compliant products banned from sale in the EU
- 2027.2.18: Digital passport for EV batteries comes into force
- 2027.8.18: Raw material due diligence obligation kicks in (two-year extension)
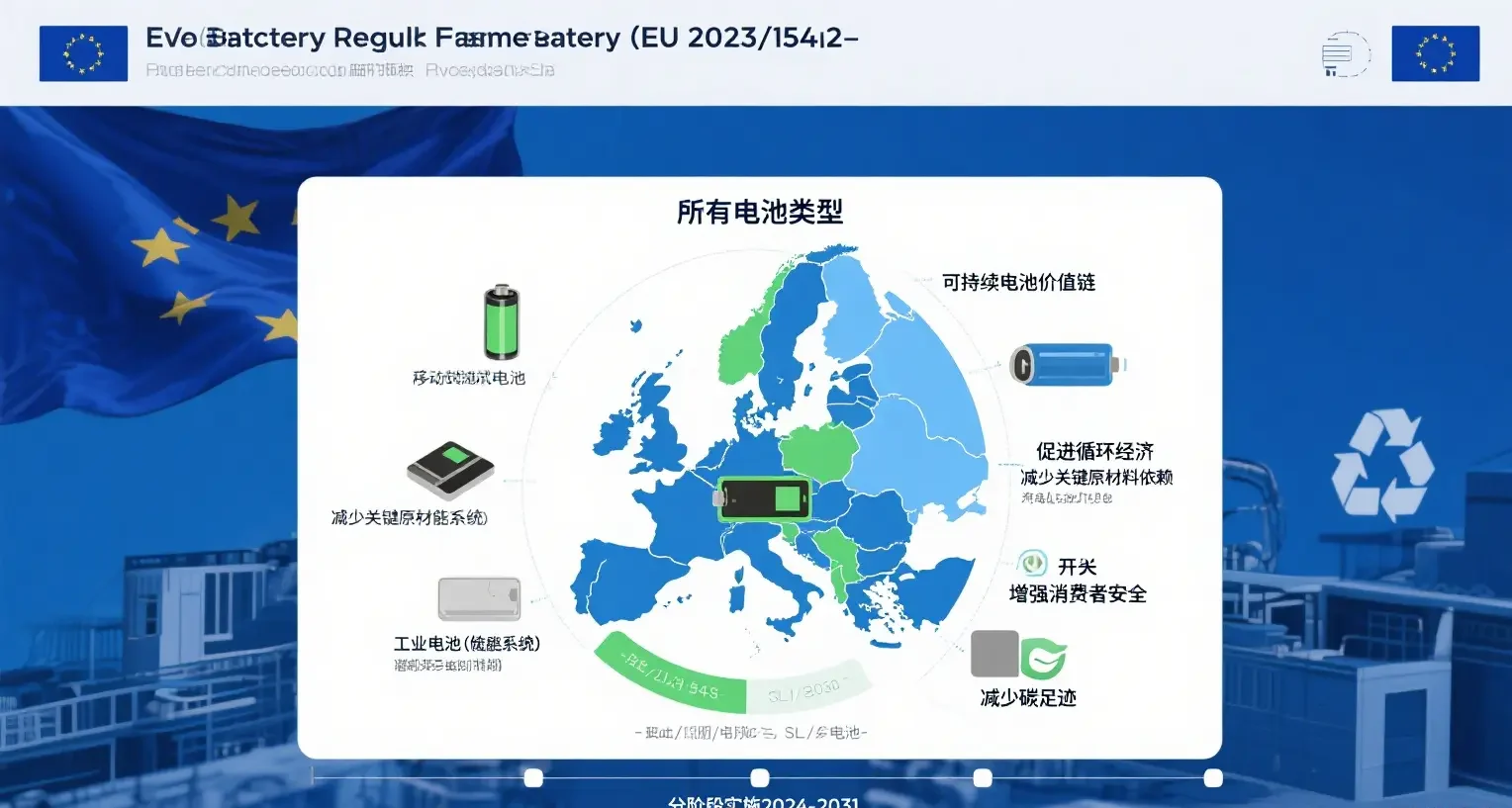
II. Technical Compliance Matrix: Differentiated Requirements for Five Types of Batteries
▶ Battery Classification and Core Obligations
| Battery type | definition | Key compliance requirements |
|---|---|---|
| portable battery | ≤5kg sealed (mobile phone/tool battery) | User-removable design (mandatory in 2027), restrictions on hazardous substances(Hg≤5ppm, Cd≤20ppm) |
| LMT battery | ≤25kg(Electric scooter/bicycle) | Digital passport, carbon footprint statement (>2kWh), recycled cobalt ≥16% |
| SLI battery | Vehicle start-stop power supply | Lead content ≤ 100 ppm, leak-proof design |
| electric vehicle battery | >25kg(power battery) | Carbon footprint threshold (2028), third-party certification, recycled lithium ≥ 6% |
| industrial battery | Stationary energy storage/backup power supply | Due diligence policy, cycle life ≥ 5000 times |
▶ Three stages of carbon footprint management
- Declaration phase (from 2025): disclosure of full life-cycle CO₂ emissions (from mining to assembly)
- Graduated labeling (from 2026): graded A-G according to carbon intensity, with a ban on sales below grade D
- Threshold limit (from 2028): power battery carbon intensity ≤ 60kg CO₂/kWh6
III. EPR registration: the cornerstone of EU market access
From August 18, 2025, all EU battery sellers must complete:
1. Producer identification:
- Non-EU companies need to designate EU Authorized Representative (EU REP)
- Cross-border e-commerce sellers need to register EPR in the country of sale (e.g., Germany, Poland, France and other 9 countries)
2. BDO system registration:
- Poland and other member states require synchronized registration of battery law + packaging law
- Get a unique EPR registration number and upload it to Amazon/Temu and other platforms.
3. Payment of recycling fee:
- Eco-disposal fee per battery weight/type (e.g. industrial batteries: €2.5/kg).
Consequences of non-compliance:
- Mandatory removal of goods from shelves (real-time monitoring by cross-border e-commerce platforms)
- Fines of up to €100,000 (Germany) or PLN 1 million (Poland)
- Supply chain disruption (Customs seizure of unregistered products)
IV.Technical Barriers: A Path for Chinese Enterprises to Attack
1. Carbon footprint optimization
- Green Power Transformation: EU thermal power accounted for <20%, China >50% → need to purchase green power certification
- Material Innovation: Silicon carbon anode replaces graphite, reducing carbon emissions from roasting process by 40%.
2. Recycling technology breakthrough
- Directional recycling process:
- Wet metallurgy lithium purity ≥99.9% (patented by Ningde Times)
- Recycled cobalt and nickel are directly supplied to anode materials, meeting the requirement of ≥16% recycling ratio.
3. Digital Passport System
- Blockchain Traceability: Docking with IBM Food Trust or VeChain platform
- Data fields include:
- Raw Material Origin (Conflict-Free Mineral Certification)
- Carbon Footprint Certificate ID
- Recycled Material Proportion Verification Code

V. Industry Impact and Strategic Recommendations
1. Rising Compliance Costs
- Third-party authentication + digital passport added cost $15-20/kWh
- SMEs at risk of elimination (exemption threshold: turnover €150 million)
2. Supply Chain Reconfiguration
- Localized production: Ningde Times Germany plant meets carbon footprint threshold
- Closed-loop recycling: Greenmax and ECOPRO build European recycling base (100,000 tons per year)
3. Technology Pre-Research Direction
- Solid-state battery exemption advantage: sulfide electrolyte without heavy metal restriction
- Removable design:
- Snap-on battery compartment (glue bonding prohibited)
- Standardized tool removal (torque ≤ 0.5Nm)